Net-Zero Buildings: A Blueprint for a Sustainable Future
Introduction
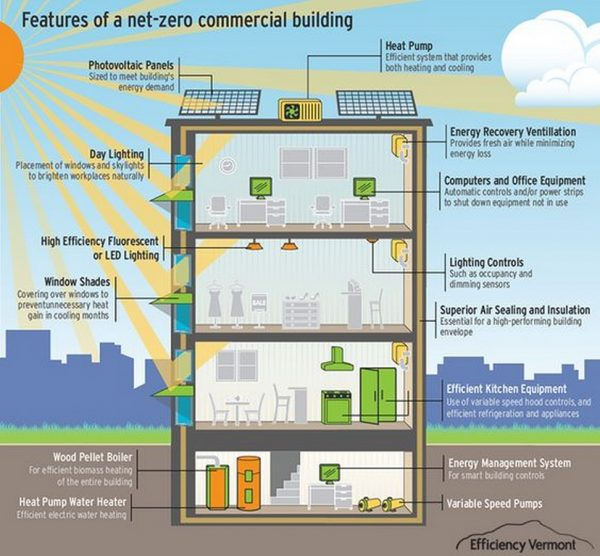
Net-zero buildings, structures that produce as much energy as they consume over the course of a year, represent a significant step towards a more sustainable future. By harnessing renewable energy sources and implementing energy-efficient design strategies, these buildings can significantly reduce their environmental impact and contribute to a cleaner, greener world.
The concept of net-zero buildings has gained significant traction in recent years, driven by growing concerns about climate change and the need to transition to a low-carbon economy. By reducing their reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing energy consumption, net-zero buildings can help to mitigate the effects of climate change and create healthier, more sustainable communities.
Achieving net-zero status requires a holistic approach that considers various aspects of building design and operation. Key strategies include incorporating passive design elements to minimize energy use, installing renewable energy systems to generate clean electricity, and implementing energy-efficient technologies to reduce consumption. Additionally, smart technology and building automation can be used to optimize energy usage and ensure that buildings operate efficiently.
While the upfront costs of constructing net-zero buildings may be higher than traditional buildings, the long-term benefits far outweigh the initial investment. Net-zero buildings can significantly reduce energy costs, improve indoor air quality, and enhance property values. Moreover, they can contribute to a more resilient and sustainable community by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
As the world continues to grapple with the challenges of climate change, net-zero buildings offer a promising path towards a more sustainable future. By embracing innovative design strategies and adopting renewable energy technologies, we can create buildings that not only reduce their environmental impact but also provide a healthier and more comfortable living and working environment for generations to come.
Key Strategies for Achieving Net-Zero
-
Energy Efficiency in Net-Zero Buildings
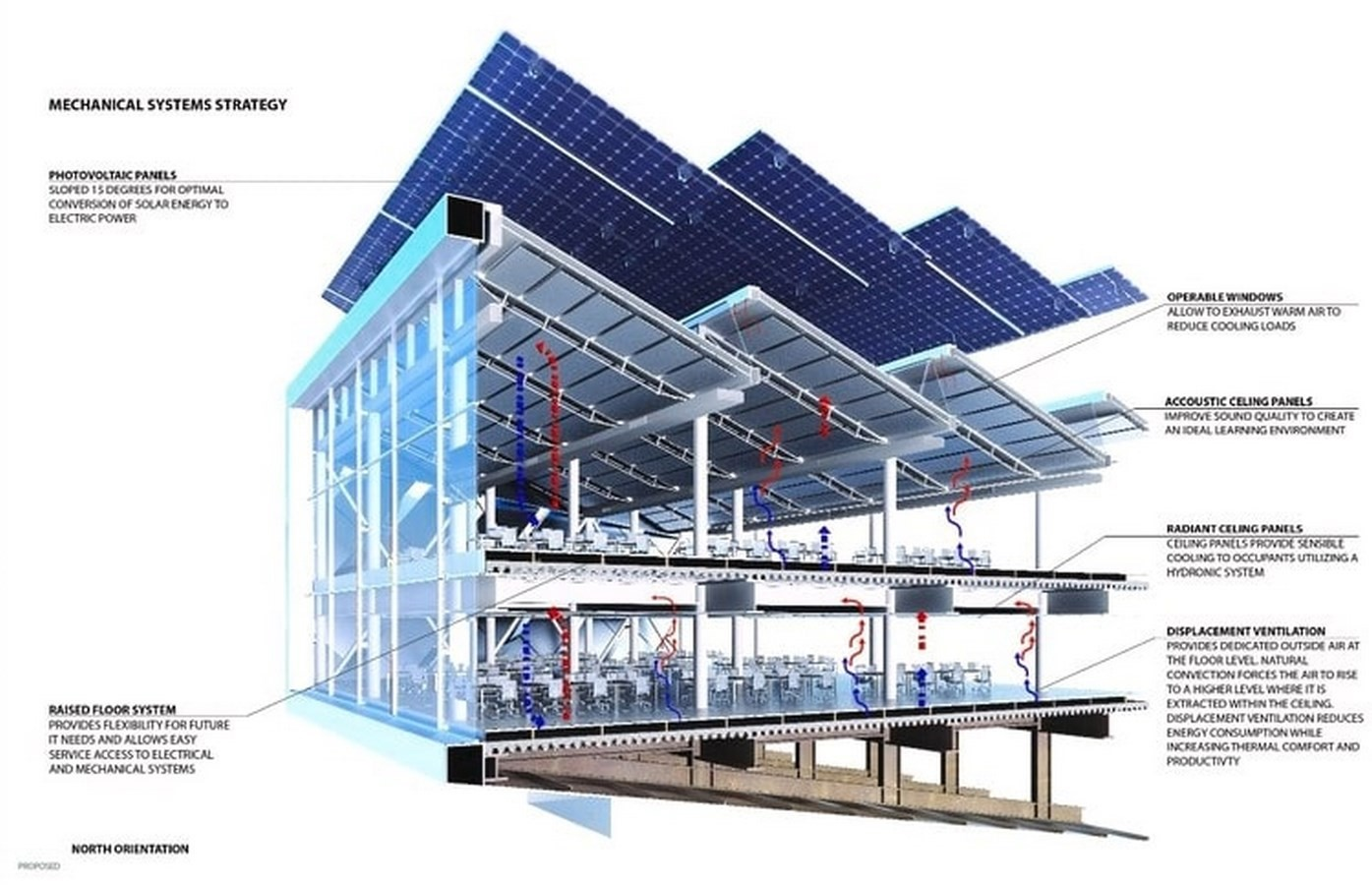
 Energy efficiency is a cornerstone of net-zero building design, aiming to minimize energy consumption while maintaining a comfortable indoor environment. By incorporating passive design strategies, installing efficient systems, and ensuring a well-insulated building envelope, architects and builders can significantly reduce the energy footprint of their projects.
Energy efficiency is a cornerstone of net-zero building design, aiming to minimize energy consumption while maintaining a comfortable indoor environment. By incorporating passive design strategies, installing efficient systems, and ensuring a well-insulated building envelope, architects and builders can significantly reduce the energy footprint of their projects.Passive Design
Passive design strategies leverage natural forces like sunlight and airflow to regulate the building's temperature and lighting. This approach can significantly reduce the need for mechanical systems and lower energy consumption.
- Shading: Strategic placement of shading elements, such as overhangs, awnings, or trees, can help block direct sunlight during peak hours, reducing cooling loads.
- Insulation: Proper insulation in walls, ceilings, and floors helps to maintain a stable indoor temperature, reducing the need for heating and cooling.
- Natural Ventilation: Designing buildings with adequate natural ventilation can help to circulate fresh air and reduce the reliance on mechanical ventilation systems.
Efficient Systems
- HVAC Systems: Installing high-efficiency heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems can significantly reduce energy consumption.
Look for systems with Energy Star ratings and consider options like geothermal heating and cooling. - Lighting: Use energy-efficient lighting fixtures, such as LED bulbs, and consider natural lighting strategies to reduce the need for artificial lighting.
- Appliances: Choose energy-efficient appliances for all your building needs, including refrigerators, dishwashers, and laundry equipment.
Building Envelope
The building envelope, which includes the walls, roof, and foundation, plays a crucial role in energy efficiency. A well-insulated building envelope can help to maintain a stable indoor temperature and reduce heat loss or gain.
- Air Sealing: Ensure that the building envelope is properly sealed to prevent air leakage, which can significantly impact energy efficiency.
- High-Performance Windows: Install high-performance windows with low-E coatings and argon gas fills to improve insulation and reduce heat transfer.
- Waterproofing: Proper waterproofing of the building envelope is essential to prevent moisture infiltration, which can lead to mold and energy loss.
By carefully considering these factors, architects and builders can design net-zero buildings that are both energy-efficient and comfortable.
- Shading: Strategic placement of shading elements, such as overhangs, awnings, or trees, can help block direct sunlight during peak hours, reducing cooling loads.
-
Renewable Energy Generation in Net-Zero Buildings
Renewable energy sources are essential for achieving net-zero status in buildings. By harnessing the power of the sun, wind, and other natural resources, buildings can reduce their reliance on fossil fuels and generate their own clean electricity.Solar Power
- Photovoltaic Panels: Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, which can be used to power the building's various systems.
- Rooftop Installations: Solar panels can be installed on the roof of the building, providing a convenient and efficient way to generate electricity.
- Ground-Mounted Systems: For larger projects, solar panels can be installed on the ground, allowing for greater flexibility in terms of location and orientation.
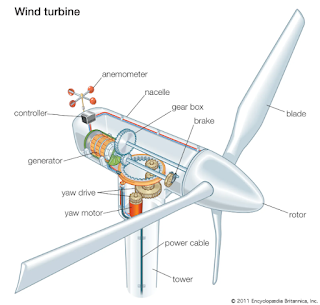
Wind Power
- Wind Turbines: Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy of the wind into electricity.
- Suitable Locations: Wind turbines are most effective in areas with consistent and strong winds.
- Community Wind Farms: Consider participating in community wind farms to share the benefits of renewable energy generation.
Other Renewable Energy Sources
- Geothermal: Harness the heat from the Earth's interior to generate electricity or provide heating and cooling.
- Biomass: Convert organic matter, such as wood waste or agricultural residues, into energy.
- Hydropower: Utilize the force of flowing water to generate electricity, if the location has suitable water resources.
The choice of renewable energy source will depend on various factors, including the building's location, size, and specific energy needs. It's important to conduct a thorough assessment to determine the most suitable options for each project.
By incorporating renewable energy generation into net-zero buildings, architects and builders can reduce their reliance on fossil fuels, contribute to a cleaner environment, and set an example for sustainable building practices.
- Photovoltaic Panels: Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, which can be used to power the building's various systems.
-
Energy Storage in Net-Zero Buildings
Energy storage systems are essential for maximizing the benefits of renewable energy generation in net-zero buildings. By storing excess energy produced during peak production periods, these systems can ensure a reliable and consistent power supply throughout the day.
Batteries
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: The most common type of battery used for energy storage in buildings. They offer high energy density and a long lifespan.
- Flow Batteries: Flow batteries store energy in electrolyte solutions, allowing for greater flexibility and scalability.
- Battery Management Systems: Advanced battery management systems are essential for optimizing battery performance and ensuring safety.
Other Energy Storage Technologies
- Thermal Storage: Thermal energy storage systems can store excess energy as heat or cold, which can be used for heating, cooling, or hot water production.
- Flywheel Storage: Flywheel storage systems store energy as rotational kinetic energy in a spinning flywheel. They offer fast response times and high efficiency.
- Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES): CAES systems store energy by compressing air into underground caverns or tanks. This technology is well-suited for large-scale energy storage applications.
The choice of energy storage technology will depend on various factors, including the building's size, energy needs, and budget. It's important to conduct a thorough assessment to determine the most suitable option for each project.
By incorporating energy storage systems into net-zero buildings, architects and builders can ensure a reliable and consistent power supply, even during periods of low renewable energy production. This helps to maximize the benefits of renewable energy and contributes to a more sustainable and resilient building.
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: The most common type of battery used for energy storage in buildings. They offer high energy density and a long lifespan.
-
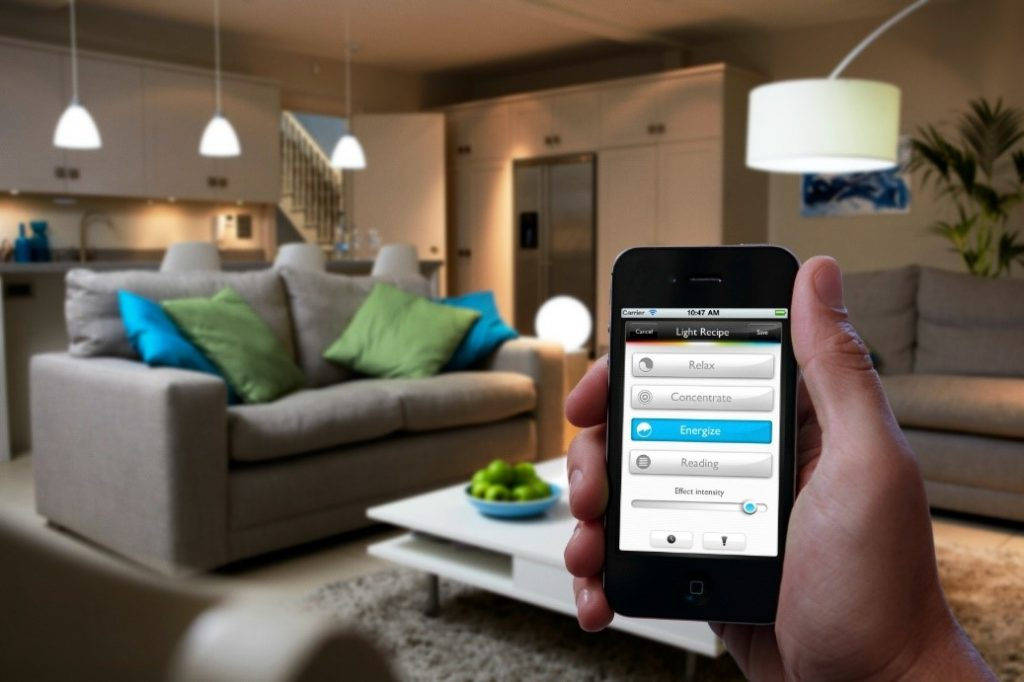
Smart Technology in Net-Zero Buildings
Smart technology plays a crucial role in optimizing energy efficiency and maximizing the benefits of renewable energy in net-zero buildings. By automating building systems and monitoring energy consumption, smart technology can help to reduce energy costs, improve comfort, and enhance overall sustainability.
Building Automation
- Lighting Control: Smart lighting systems can automatically adjust lighting levels based on occupancy, daylight conditions, and other factors, reducing energy consumption and improving occupant comfort.
- HVAC Control: Building automation systems can optimize the operation of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems to ensure efficient and comfortable indoor environments.
- Shade Control: Smart shading systems can automatically adjust window shades and blinds to control sunlight and reduce cooling loads.
Energy Management Systems
- Real-Time Monitoring: Energy management systems can provide real-time data on energy consumption, allowing building operators to identify areas for improvement and optimize energy use.
- Demand Response: These systems can help buildings participate in demand response programs, reducing energy consumption during peak demand periods and lowering energy costs.
- Predictive Analytics: Energy management systems can use predictive analytics to anticipate energy usage patterns and optimize building operations accordingly.
By incorporating smart technology into net-zero buildings, architects and builders can create more intelligent, efficient, and sustainable structures. These technologies can help to maximize the benefits of renewable energy, reduce energy costs, and improve occupant comfort and satisfaction.
- Lighting Control: Smart lighting systems can automatically adjust lighting levels based on occupancy, daylight conditions, and other factors, reducing energy consumption and improving occupant comfort.
Benefits of Net-Zero Buildings
Net-zero buildings offer a wide range of benefits for both individuals and communities. By reducing energy consumption and generating their own clean energy, these buildings contribute to a more sustainable future while providing economic, health, and social advantages.
Environmental Impact
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Net-zero buildings significantly reduce their carbon footprint by minimizing reliance on fossil fuels and generating clean energy. This helps to mitigate climate change and protect the environment.
- Improved Air Quality: By reducing the use of fossil fuels, net-zero buildings can help to improve air quality and reduce pollution.
- Water Conservation: Many net-zero building strategies incorporate water-saving measures, such as rainwater harvesting and efficient irrigation systems, further reducing their environmental impact.
Economic Benefits
- Lower Energy Costs: Net-zero buildings can significantly reduce energy bills, saving money for building owners and occupants.
- Increased Property Values: Properties with net-zero certifications often have higher property values due to their increased desirability and potential for reduced operating costs.
- Job Creation: The construction and operation of net-zero buildings can create jobs in the renewable energy and green building sectors.
Improved Health and Comfort
- Indoor Air Quality: Net-zero buildings often prioritize indoor air quality by incorporating ventilation systems and using non-toxic materials. This can improve the health and well-being of occupants.
- Thermal Comfort: By optimizing energy efficiency and incorporating passive design strategies, net-zero buildings can provide a more comfortable indoor environment, reducing the need for excessive heating or cooling.
- Reduced Noise Pollution: Many net-zero building strategies include noise-reducing measures, such as soundproofing and insulation, creating a quieter and more peaceful living environment.
Community Resilience
- Energy Independence: Net-zero buildings reduce reliance on the grid, making communities more resilient to power outages and energy price fluctuations.
- Emergency Preparedness: These buildings can serve as community hubs during emergencies, providing shelter, power, and other essential services.
- Community Leadership: Net-zero buildings can inspire other community members to adopt sustainable practices and contribute to a more resilient and environmentally friendly future.
By embracing net-zero construction, communities can create more sustainable, resilient, and healthy environments for future generations
Challenges and Considerations for Net-Zero Buildings
While net-zero buildings offer numerous benefits, there are also challenges and considerations to be addressed:
Initial Costs
- Upfront Investment: Implementing net-zero strategies often requires a higher upfront investment compared to traditional construction methods. This includes the cost of installing renewable energy systems, energy-efficient equipment, and advanced building technologies.
- Return on Investment: While the long-term benefits of net-zero buildings can outweigh the initial costs, it's essential to carefully consider the potential return on investment and payback period.
Local Regulations and Incentives
- Government Support: Explore government incentives and regulations that support net-zero construction in your area. This can include tax credits, rebates, and financing options.
- Zoning and Building Codes: Ensure that local zoning and building codes are compatible with net-zero construction standards.
- Policy Advocacy: Advocate for policies that promote net-zero construction and create a favorable environment for sustainable development.
Technological Advancements
- Emerging Technologies: Stay updated on the latest advancements in energy-efficient technologies, such as new materials, building systems, and renewable energy sources.
- Integration and Compatibility: Ensure that the chosen technologies are compatible with each other and can be effectively integrated into the building design.
- Risk Management: Consider the potential risks associated with new technologies and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Maintenance and Operation
- Ongoing Maintenance: Net-zero buildings require ongoing maintenance to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency. This includes regular inspections, cleaning, and repairs.
- Operator Training: Provide training to building operators and maintenance staff to ensure they understand and can effectively operate the building's systems.
- Monitoring and Optimization: Use monitoring systems to track energy consumption and identify areas for improvement, allowing for ongoing optimization of the building's performance.
By carefully considering these challenges and taking proactive steps to address them, architects, builders, and building owners can successfully implement net-zero strategies and create sustainable, efficient, and profitable projects.














































![Terry Farrell [ British architect]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgF5Bc7-F6oyGHwVlcJfUVoN9PAph8ZIAQAVTMDZ0oOX0kIENEGN84Arj8wxKS666_yV2hRHMM4zlJ5gCJFBA1ttvrGBPrCNY0tZWfcuPl0aolt_szKpBjWtbLYutI4ivHBLrzZkj-wEk_l_1paoEEVkgnzCt7yvpHoDkhm63TxHxL45GUgV2OZVkwLYkWG/w100/11e81b6d-862f-4a23-a2d0-950d22063de0.png)



0 Comments